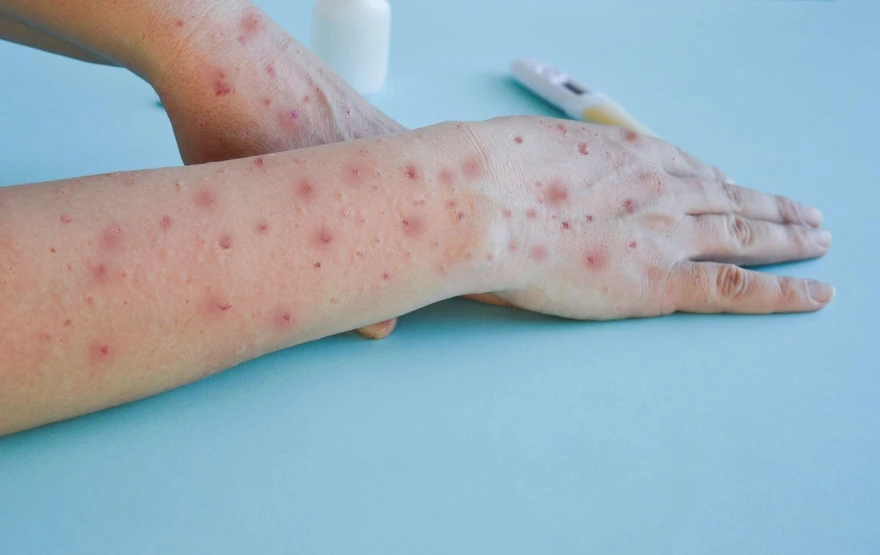
Mpox, also known as Monkeypox, is a zoonotic viral disease that originated in primates and subsequently spread to humans. First identified in 1958 among laboratory monkeys, this disease has become an important public health issue due to its potential for outbreaks. The virus is a cousin of the variola virus that causes smallpox, though it generally presents with milder symptoms. It is classified within the Orthopoxvirus genus, placing it among a group of viruses that share similar biological properties.
The mpox virus affects the body by entering through broken skin, respiratory tract, or mucous membranes, and it can lead to a range of symptoms. These include fever, intense headache, lymphadenopathy (swelling of the lymph nodes), back pain, myalgia (muscle aches), and an acute rash characterized by pustular lesions. These lesions go through various stages before finally crusting and falling off. The incubation period for mpox can range from 5 to 21 days, which contributes to difficulties in diagnosing the disease promptly.
Understanding the trail of mpox is paramount for effective treatment and prevention. Given its capacity to affect both humans and animals, comprehensive knowledge about this virus helps in orchestrating a multi-faceted approach to its control. Mpox can have significant health implications, particularly for individuals with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, and young children, who may experience more severe manifestations of the disease.
This makes it essential to raise awareness about the symptoms and transmission modes of mpox. Effective and timely diagnosis not only aids in mitigating its spread but also enables healthcare providers to administer appropriate treatment strategies. Efforts to comprehend mpox deeply are indispensable in facilitating global health security, minimizing outbreak potential, and fostering community resilience against this zoonotic disease.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Mpox
Mpox, a viral infection, often presents with distinct symptoms which, when recognized early, can significantly enhance the efficacy of treatment. Among the most notable symptoms are skin rashes, which typically begin as red spots and progress to more pronounced rashes or pustules. These rashes primarily appear on the face and extremities but may also spread to other parts of the body.
Fever is another common symptom of Mpox. It often precedes the appearance of rashes and can range from mild to severe. Accompanying the fever, individuals might experience chills, muscle aches, and headaches. These systemic symptoms are indicative of the body’s response to the viral infection, signaling that the immune system is actively combating the virus.
In addition to skin rashes and fever, other physical manifestations can include swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpits, or groin. This swelling is a direct result of the body’s immune response and can aid in differentiating Mpox from other viral infections which do not typically cause lymphadenopathy.
Variations in symptoms may occur based on age, health status, and other factors. For instance, younger children and older adults might exhibit more severe symptoms due to a less robust immune system. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions or compromised immunity may also experience more intense and prolonged symptoms.
Early recognition of Mpox symptoms is crucial. Prompt identification allows for timely medical intervention, which can mitigate the severity of the infection and prevent complications. It is essential for individuals to not only be aware of the common symptoms but also to understand the importance of seeking medical advice if they suspect they have been exposed to the virus.
Initial Steps for Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of mpox is critical for effective treatment and management. The diagnostic process generally begins with a detailed patient history and physical examination conducted by healthcare providers. This initial step helps in identifying the characteristic symptoms of mpox, which include fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy, among others. However, due to symptom overlap with other conditions, further medical tests are essential for confirming the diagnosis.
Blood tests are commonly used in the diagnosis of mpox. These tests can detect the presence of mpox virus (MPXV) DNA in the patient’s blood, providing a reliable indicator of infection. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests are highly sensitive and specific, making them a gold standard for detecting viral infections, including mpox. In some cases, serological tests may also be performed to identify antibodies against the mpox virus, indicating a past or current infection.
Another crucial diagnostic tool is a skin biopsy. This involves removing a small sample of the affected skin area, which is then examined under a microscope. The biopsy can reveal characteristic changes in skin cells caused by the mpox virus, aiding in a definitive diagnosis. Dermatologists and pathologists play a pivotal role in interpreting these biopsy results accurately.
The role of healthcare providers extends beyond the identification of mpox symptoms. They must also perform a differential diagnosis to rule out other illnesses with similar clinical presentations, such as chickenpox, smallpox, and certain skin infections. Differential diagnosis involves comparing clinical findings, laboratory test results, and patient history with the characteristics of other potential conditions. This thorough approach ensures that the correct diagnosis is made, allowing for appropriate treatment to be administered.
In conclusion, the combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and skin biopsies, along with differential diagnosis, forms a comprehensive strategy for diagnosing mpox. Healthcare providers are indispensable in guiding patients through this process, ensuring timely and accurate identification of the condition.
Treatment Options for Mpox Symptoms
The therapeutic approach towards managing Mpox varies dependiendo the severity of the infection. For mild cases, supportive care often suffices. This includes over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to alleviate fever and discomfort, as well as ensuring adequate hydration and rest. It is crucial to maintain proper hygiene practices to prevent secondary infections, which can complicate the course of Mpox.
Antiviral drugs may be prescribed for more moderate to severe manifestations of Mpox. Tecovirimat, also known as TPOXX, is one such antiviral medication that has been authorized for use against Mpox under specific conditions. Brincidofovir is another antiviral agent that has shown efficacy against orthopoxviruses, the family to which Mpox belongs. Prescribing these medications necessitates careful consideration by healthcare professionals, weighing potential benefits against possible side effects.
In the realm of preventive measures, vaccines may play an instrumental role. Although no vaccine is specifically formulated for Mpox, the smallpox vaccine has demonstrated cross-protection due to the genetic similarities between the viruses. The use of the smallpox vaccine in preventing Mpox is particularly emphasized for individuals who are at high risk, including healthcare workers and close contacts of infected persons.
For severe cases of Mpox, hospitalization might be required to provide intensive supportive care. This can include intravenous fluids, potent pain management strategies, and close monitoring of vital signs. Certain patients may necessitate respiratory support if pulmonary complications arise. Early recognition and management of symptoms become paramount in such instances to mitigate morbidity.
Beyond conventional medical treatments, some alternative therapies are suggested by proponents, though it’s essential to approach these with caution due to the limited empirical evidence supporting their efficacy. Such alternatives might include herbal remedies and immune-boosting supplements. Consulting with a healthcare provider before initiating any alternative therapy is vital to ensure it does not interfere with standard medical treatments.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Changes
Proper nutrition and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in the treatment and recovery process of mpox. A balanced diet is essential for bolstering the immune system, which is instrumental in fighting off the infection. A well-rounded diet should include an array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These food groups provide the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants required for optimal immune function.
Staying hydrated is another key aspect of managing mpox. Hydration aids in maintaining electrolyte balance and overall bodily functions, including the immune response. It’s advisable to consume at least eight glasses of water per day, alongside hydrating foods such as cucumbers, oranges, and watermelons. Herbal teas and broths can also be beneficial, providing warmth and comfort while aiding hydration.
Adequate rest is vital for recovery from mpox. Quality sleep helps to repair and regenerate the body, facilitating a stronger immune response. Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night, ensuring their sleep environment is conducive to rest – this includes a dark, quiet, and cool setting.
Certain foods can greatly boost immune function. Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich in Vitamin C, known for its immune-enhancing properties. Garlic and ginger, with their anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial characteristics, can be integrated into meals to support health. Probiotic-rich foods such as yogurt and kefir help maintain gut health, which is closely linked to immune strength.
Conversely, it’s important to avoid foods that could potentially impair immune function. Highly processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive caffeine can all hinder the body’s ability to fight infections effectively. Limiting alcohol intake is also advised, as it can suppress the immune system.
Implementing these nutritional and lifestyle changes not only aids in recovery but also promotes long-term health, fortifying the body against future infections. Adopting these habits ensures a holistic approach to managing and curing mpox.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing Mpox, also known as monkeypox, requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses personal hygiene practices, vaccination, and strategies to minimize exposure in high-risk areas. These measures are designed to protect individuals and communities, ensuring public health safety.
Firstly, personal hygiene is paramount in preventing the contraction and spread of Mpox. Regular handwashing with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer is highly recommended. It is also advisable to avoid touching your face, especially the eyes, nose, and mouth, with unwashed hands. In addition, maintaining cleanliness in living and workspaces by disinfecting frequently-touched surfaces can substantially reduce the risk of infection.
Vaccination remains one of the most effective strategies against Mpox. The smallpox vaccine has been shown to provide a high level of protection against Mpox due to the genetic similarities between the two viruses. Health authorities recommend vaccination for individuals in high-risk groups, such as healthcare workers or those living in areas with reported cases. Keeping up to date with vaccinations can significantly reduce the likelihood of contracting the virus.
To avoid exposure in high-risk areas, individuals should be cautious when traveling to regions where Mpox outbreaks have been reported. Staying informed through travel advisories and health alerts issued by local and international health organizations is crucial. Travelers should also avoid direct contact with animals, particularly rodents and primates, that may harbor the virus, and refrain from consuming undercooked meat or wild game that could be contaminated.
Community and public health measures play a vital role in preventing the spread of Mpox. Public health authorities often implement policies such as quarantine for individuals exposed to the virus and enforce travel restrictions during outbreaks. Additionally, widespread education campaigns aimed at raising awareness about preventative practices and symptoms can empower communities to take proactive measures.
By adhering to these prevention strategies, individuals and communities can significantly mitigate the risk of contracting and spreading Mpox, thereby safeguarding public health.
Caring for Someone with Mpox Symptoms
Caring for someone diagnosed with Mpox involves a multifaceted approach that addresses emotional, physical, and logistical needs. As a caregiver, it’s essential to manage these aspects effectively to ensure the well-being of both the patient and yourself. Understanding infection control measures, managing medical treatments at home, and providing emotional support are crucial components in this caregiving journey.
Firstly, infection control is paramount to prevent the spread of Mpox. Caregivers should regularly wash their hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. When soap and water aren’t available, an alcohol-based hand sanitizer can be used. It’s vital to clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces daily, including doorknobs, light switches, and countertops. Caregivers should also use personal protective equipment such as gloves and masks, especially when handling the patient’s bodily fluids or items they have used.
Managing medical treatments at home involves following the healthcare provider’s instructions diligently. This includes administering any prescribed medications on schedule and monitoring the patient for any changes in their condition. Understanding the symptoms of Mpox, such as fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes, can help in assessing the patient’s progress. If the patient experiences severe symptoms or complications, don’t hesitate to seek medical attention immediately.
Providing emotional support is another critical aspect of caregiving for someone with Mpox. Patients may experience anxiety, stress, or depression due to their illness. Offering a listening ear, reassurance, and being present can significantly help in alleviating their emotional distress. Encourage open communication, and ensure that the patient feels comfortable expressing their feelings and concerns. Additionally, maintaining a calm and positive environment can contribute to their overall mental well-being.
Balancing these components—infection control, medical management, and emotional support—will contribute significantly to the patient’s recovery journey while also ensuring the caregiver’s health and safety. By staying informed and prepared, caregivers can effectively manage the challenges that come with caring for someone with Mpox.
When to Seek Professional Help
While the majority of mpox cases may resolve on their own with adequate self-care and home remedies, there are certain conditions under which seeking professional medical help becomes imperative. Recognizing these conditions early can make a significant difference in the management and outcome of the disease.
Firstly, if you notice a rapid worsening of symptoms or severe discomfort, it is crucial to contact a healthcare provider. Signs such as high fever, extensive rash that covers large areas of the body, or pain that becomes unmanageable with over-the-counter medications require professional evaluation. Additionally, if the mpox rash shows signs of secondary bacterial infection—such as increased redness, warmth, pus, or swelling—it necessitates immediate medical attention.
Visiting an emergency room is advised if you experience any symptoms indicative of a life-threatening condition. This includes difficulty breathing, chest pain, confusion, and an inability to stay awake. These symptoms could signify a severe and rapidly progressing form of the disease, or they could be indicative of complications such as pneumonia or sepsis.
For individuals with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, compromised immune systems, or chronic respiratory diseases, early consultation with a specialist is highly recommended. These conditions can exacerbate the severity of mpox, making tailored medical advice and intervention crucial. Pregnant women and young children should also receive prompt medical care to mitigate risks to themselves and, in the case of pregnant women, to the unborn child.
Moreover, follow-up appointments and ongoing monitoring play a vital role in ensuring the disease is managed effectively. Regular consultations allow healthcare providers to assess the treatment’s efficacy, monitor for potential complications, and adjust care plans as necessary. Persistent or recurring symptoms should not be ignored; continual monitoring safeguards against long-term health impacts and aids in timely recovery.
Understanding Mpox: A Comprehensive Guide
Mpox, formerly known as Monkeypox, is a rare viral illness that can cause a rash and other flu-like symptoms. While it is not as contagious as COVID-19, it is important to be aware of the symptoms, transmission, and prevention methods.
What is Mpox?
Mpox is a viral infection that can be transmitted through close contact with an infected person or animal. It is caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox.
Symptoms of Mpox Symptoms
The symptoms of Mpox typically appear within 7 to 21 days after exposure. They may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Rash
The rash usually starts on the face and spreads to other parts of the body. It can be itchy and painful.
Transmission of Mpox Symptoms
Mpox can be transmitted through:
- Close contact with an infected person’s rash, scabs, or bodily fluids
- Contact with contaminated materials, such as bedding or clothing
- Respiratory droplets from an infected person (rare)
Prevention of Mpox
While there is no cure for Mpox, there are ways to prevent its spread. These include:
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Washing your hands frequently with soap and water
- Practicing good hygiene
- Getting vaccinated against smallpox (can provide some protection against Mpox)
If you are concerned about Mpox or have any symptoms, please seek medical attention immediately.
FAQs:
Q: What is the difference between Mpox and smallpox?
A: Mpox is caused by the monkeypox virus, while smallpox is caused by the variola virus. Smallpox has been eradicated worldwide, but Mpox continues to circulate in some parts of the world.
Q: Is Mpox contagious?
A: Yes, Mpox is contagious. It can be spread through close contact with an infected person or animal.
Q: What are the risk factors for Mpox?
A: The risk factors for Mpox include:
- Close contact with an infected person or animal
- Travel to areas where Mpox is endemic
- Immune system compromise
Q: Is there a vaccine for Mpox?
A: There is no specific vaccine for Mpox, but the smallpox vaccine can provide some protection.
Q: How is Mpox treated?
A: There is no specific treatment for Mpox. However, supportive care, such as pain relievers and fluids, can help manage symptoms.
Please remember that the information provided here is for general knowledge only. For any health concerns, please consult with a healthcare professional.
Vatave Healthcare is committed to providing comprehensive healthcare solutions. We offer a wide range of services, including [list of services]. Visit our website or contact us to learn more.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns.